หากเราต้องการจัดกลุ่มอะไรสักอย่าง เช่น ภาพยนตร์ เราก็แค่แยกมันตามป้ายประเภท (Label) ที่ติดกำกับไว้ ไม่ว่าจะเป็น แอ็กชั่น ไซไฟ มิวสิคัล คอมมิดี้ โรแมนติก ดราม่า อื่น ๆ แล้วถ้าเราต้องการแบ่งกลุ่มอะไรสักอย่างที่ไม่มี label ล่ะ เช่น กองเอกสารที่ไม่เคยถูกกำหนดประเภทไว้ เราจะรู้ได้ยังไงว่ามันมีกี่ประเภทและเป็นประเภทอะไรบ้าง หากกองเอกสารมีแค่ 10-20 ฉบับก็คงง่าย เราสามารถอ่านทีละเล่มแล้วพิจารณาแบ่งกลุ่มประเภทได้ แต่ถ้ากองเอกสารที่ว่ามีจำนวนมากกว่า 1,000 ฉบับล่ะ?
สิ่งที่เราควรทำคือให้ Machine Learning แยกกลุ่มให้เรา เทคนิคนี้เรียกว่า Clustering ซึ่งจัดอยู่ในประเภทของการเรียนรู้แบบไม่มีผู้สอน (Unsupervised Learning) เมื่อเราได้กลุ่มเอกสารที่เครื่องแยกไว้ให้เราแล้ว เราก็ค่อยเข้าไปดูลักษณะของแต่ละกลุ่มและกำหนดชื่อให้กลุ่มนั้น ๆ ตัวอย่างของการทำ Clustering ก็เช่น การแบ่ง segment ลูกค้า ที่ปัจจุบันมีการเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรมไปเรื่อย ๆ จนเราไม่สามารถกำหนดลักษณะของ segment ที่ตายตัวได้
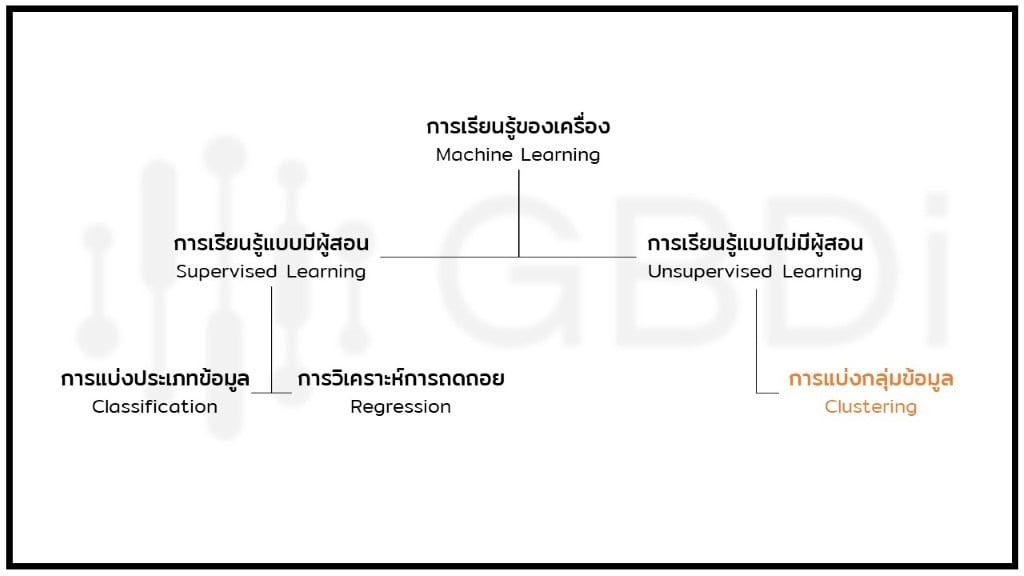
Clustering Algorithms มีหลากหลายประเภท ในบทความนี้เราจะมาทำความรู้จักกับ 4 ประเภทหลัก ๆ พร้อมตัวอย่างการนำไปใช้งานกันครับ
1. Centroid-based Clustering
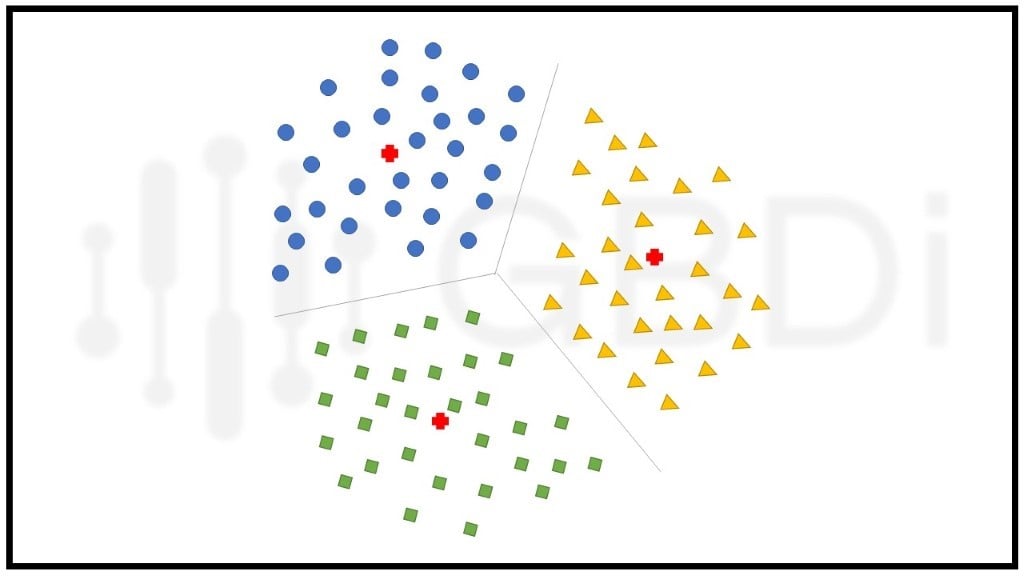
การแบ่งกลุ่มของข้อมูลเกิดจากจุดข้อมูล (Data Point) ที่กระจุกตัวใกล้กับจุดกึ่งกลางของกลุ่ม (Centroid) มากที่สุด การแบ่งกลุ่มแบบนี้มีประสิทธิภาพแต่ก็มีความอ่อนไหวขึ้นกับเงื่อนไขตั้งต้นและข้อมูลที่เป็น outlier ซึ่ง algorithm ที่นิยมใช้และถูกกล่าวถึงบ่อยครั้ง คือ k-means เพราะเป็น algorithm ที่ง่ายและมีประสิทธิภาพ โดยมีการทำงานแบบ iterative คือวนซ้ำ ๆ เพื่อคำนวณระยะห่าง หรือ Euclidean Distance ของ data point กับ centroid ในแต่ละกลุ่ม ผลที่ได้คือ data point ที่อยู่ใกล้กับ centroid ไหนมากที่สุด ก็จะถูกจัดให้อยู่กลุ่มเดียวกันกับ centroid นั้นมีข้อควรระลึกไว้คือ ผลลัพธ์จากการใช้ k-means ในแต่ละครั้งจะไม่เหมือนกันเนื่องจากการกำหนด centroid ในขั้นแรกสุดนั้นเป็นการสุ่ม
ตัวอย่างการใช้งาน เช่น การแบ่ง segment ของลูกค้าในประเภทธุรกิจต่าง ๆ, การแบ่งกลุ่มเอกสารที่ไม่มีประเภทระบุ, การแนะนำสินค้าที่ลูกค้ามีโอกาสจะซื้อ เป็นต้น
ขอแนะนำบทความที่น่าสนใจเกี่ยวกับ k-means algorithm
2. Density-based Clustering
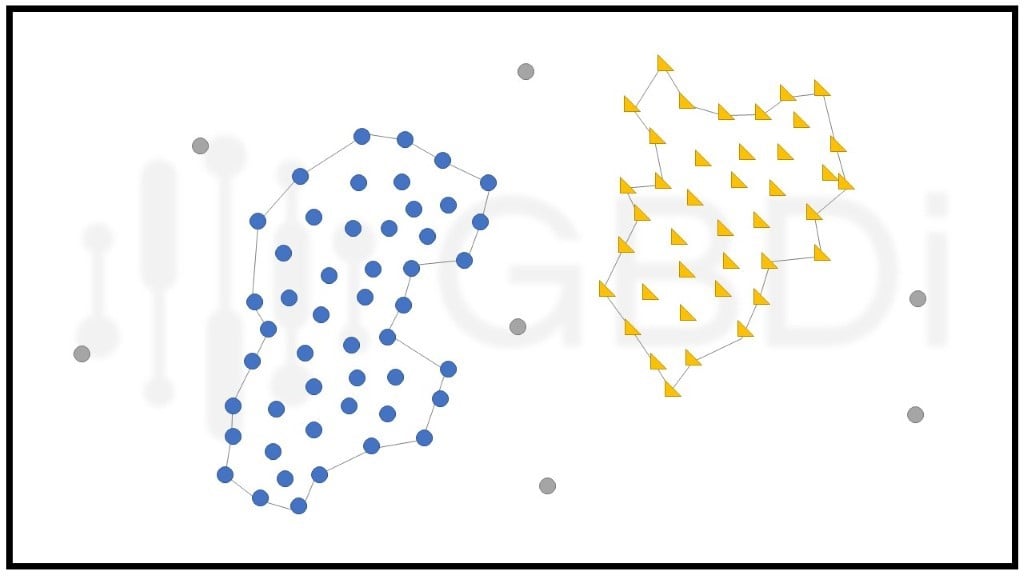
การแบ่งกลุ่มของข้อมูลเกิดจากการกระจุกตัวของ data point ที่เกาะกันอย่างหนาแน่นและไม่เป็นรูปลักษณ์ที่ตายตัว อุปสรรคของการแบ่งกลุ่มแบบนี้คือ ความหนาแน่นที่ผันผวนและจำนวน feature ของชุดข้อมูล นอกจากนี้ยังแยก outlier ออกจากกลุ่มได้ชัดเจนด้วย ถือว่าข้อดีและเป็นการแก้ข้อบกพร่องของ centroid-based model ที่ sensitive กับ outlier ซึ่ง algorithm ที่นิยมใช้ คือ DBSCAN (Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise) ในขั้นแรก กำหนดรัศมีจากจุดศูนย์กลาง (eps) และจำนวน data point ขั้นต่ำในรัศมี (MinPts) จากนั้นถ้า data point ที่เป็นจุดศูนย์กลางรวมกับ data point ที่อยู่โดยรอบภายในวงรัศมีมีจำนวนเท่ากับ MinPts เราจะเรียก data point จุดนั้นว่า “core point” ส่วน “border” คือ data point ที่เป็นจุดศูนย์กลางและมี data point ที่อยู่โดยรอบกับ core point หรือ border ด้วยกันเอง พูดง่าย ๆ คือจะรวมจุดที่เป็นเพื่อนของเพื่อนของเพื่อนไปเรื่อย ๆ จนไม่มีเพื่อนให้จับกลุ่มอีกแล้ว ก็จะถือว่าสิ้นสุดการจับกลุ่ม ส่วนจุดที่ไม่ถูกจับรวมกลุ่มเพราะอยู่ไกลเกินไปจะถือว่าเป็น outlier หรือ noise
ตัวอย่างการใช้งาน เช่น Anomaly Detection ที่มีมากกว่า 1 ตัวแปร เป็นต้น
3. Distribution-based Clustering
การแบ่งกลุ่มประเภทนี้สันนิษฐานว่าข้อมูลมีรูปแบบการแจกแจงแบบใดแบบหนึ่ง เช่น การแจกแจงปกติ (Normal Distributions) เมื่อระยะห่างระหว่างจุดศูนย์กลางของการแจกแจง กับ data point เพิ่มมากขึ้น ความน่าจะเป็นที่ data point เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของการแจกแจงนั้นจะลดลง แต่ถ้าเราไม่ทราบว่าข้อมูลมีการแจกแจงแบบใด ก็ควรเลือกใช้การ clustering รูปแบบอื่น ซึ่ง algorithm ที่เป็นตัวอย่าง คือ Expectation-maximization algorithm หรือเรียกว่า EM algorithm ซึ่งมีการทำงานแบบ iterative ระหว่าง 2 โหมด คือ E-Step ประมาณการค่าของตัวแปรที่หายไปจากชุดข้อมูล และ M-Step เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพพารามิเตอร์ของโมเดล
ตัวอย่างการใช้งาน เช่น การตรวจสอบหาการทุจริต (Fraud Detection)
4. Hierarchical Clustering
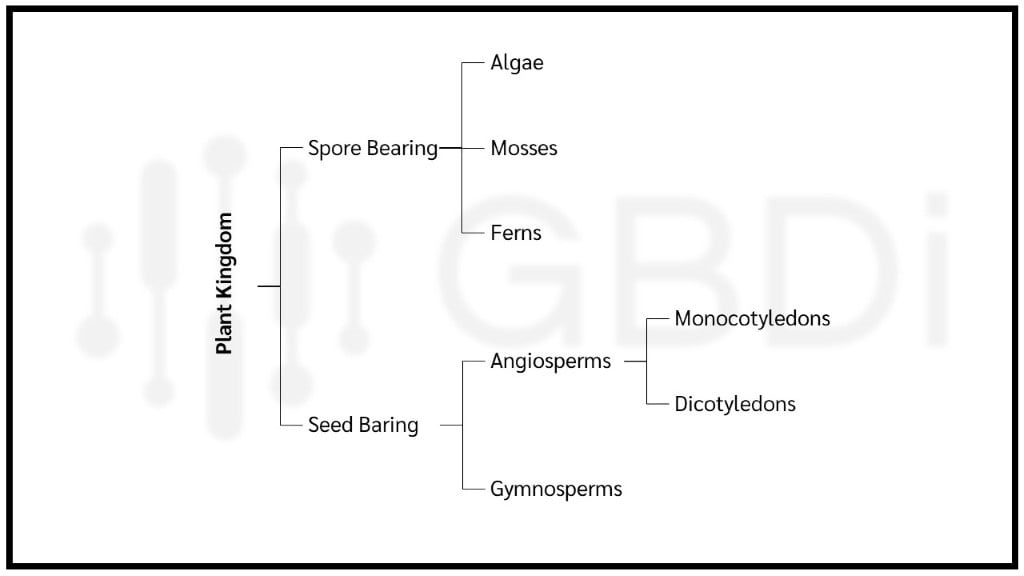
การแบ่งกลุ่มประเภทนี้จะสร้างให้เกิดต้นไม้ของกลุ่มข้อมูลขึ้น เหมาะสำหรับข้อมูลที่มีลำดับชั้น เช่น อนุกรมวิธาน (Taxonomy) การแบ่งกลุ่มลักษณะนี้มี 2 ประเภท คือ ล่างขึ้นบน (Agglomerative) และ บนลงล่าง (Divisive) ดังนี้
- Agglomerative – ในเริ่มแรก data point นั้นนับเป็นหนึ่ง cluster จากนั้นจะคำนวณหาค่าความใกล้ชิด cluster ที่อยู่ใกล้กันจะถูกจับรวมตัวกัน และจะวนทำเช่นนี้ไปเรื่อย ๆ จนกว่าจะกลายเป็น cluster เดียวในที่สุด แผนภาพที่ถูกใช้นำเสนอการทำ cluster เช่นนี้ คือ Dendrogram
- Divisive – เทคนิคนี้จะทำตรงกันข้ามกับ Agglomerative คือเริ่มจาก cluster กลุ่มใหญ่กลุ่มเดียว และแยกกลุ่มที่ไม่เหมือนกันออกไปเรื่อย ๆ จะเป็นเป็น n กลุ่มที่แยกต่อไม่ได้แล้ว
ตัวอย่างกันใช้งาน เช่น การแบ่งกลุ่มพืช หรือสิ่งมีชีวิต, การแบ่งกลุ่มสินค้า
สรุป
การทำ clustering มีหลากหลายวิธี แต่ 4 ตัวอย่างที่ยกมานี้เป็นการแบ่ง cluster ที่พบได้ทั่วไป เราควรเลือกใช้การแบ่ง cluster ประเภทใดนั้นขึ้นอยู่กับโจทย์ของเรา เมื่อเราแบ่ง cluster แล้ว ขั้นตอนต่อไปคือการประเมิน cluster ที่เราแบ่ง ว่ามีคุณภาพเป็นอย่างไร แล้วเราจะสามารถปรับ parameters เพื่อให้ดีขึ้นได้แค่ไหน เราจะอธิบายเรื่องนี้ในโอกาสต่อไปครับ
ที่มา
- Clustering Algorithms
https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/clustering/clustering-algorithms - Different Types of Clustering Algorithm
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/different-types-clustering-algorithm/ - A Gentle Introduction to Expectation-Maximization (EM Algorithm)
https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2019/10/gaussian-mixture-models-clustering/ - Understanding the concept of Hierarchical clustering Technique
https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-the-concept-of-hierarchical-clustering-technique-c6e8243758ec
Partnership Specialist
Big Data Institute (Public Organization), BDI
- Saksit Srimaronghttps://bdi.or.th/en/author/saksit-sr/11 August 2022
- Saksit Srimaronghttps://bdi.or.th/en/author/saksit-sr/28 February 2022
- Saksit Srimaronghttps://bdi.or.th/en/author/saksit-sr/28 May 2021
- Saksit Srimaronghttps://bdi.or.th/en/author/saksit-sr/25 December 2020